Lung fibrosis in vivo:
Pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic, progressive lung disease with high morbidity and mortality. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis is the most widely known and best-characterized in vivo model of human lung fibrosis. Our rodent models are induced by intratracheal administration of Bleomycin, which initially leads to lung injury accompanied by an inflammatory response and develops into lung fibrosis.
We offer assessments of the potency and anti-fibrotic efficacy of your candidate compound(s) by exploring clinically relevant pulmonary function parameters (e.g., resistance and compliance) and histopathology read-outs. Furthermore, the Standard of Care (SoC) compound Nintedanib can be used as a therapeutic reference. We can apply your test compound(s) by various application routes (e.g., oral, subcutaneous, intratracheal, intranasal, intraperitoneal, intravenous, osmotic pumps, etc.).
Read-outs:
- Lung function testing (e.g., compliance, resistance, elastance)
Lung histopathology, including Ashcroft scoring
- Immunohistochemistry (Col1A1)
- Bronchoalveolar (BAL) fluid analysis with leukocyte counts
- Hydroxyproline analysis (BAL, lung)
- µCT imaging of the lung
- Biomarker analysis (ELISA, qPCR)
- PK and/or PK/PD analysis
Get in touch with our scientific experts. If you are interested in other respiratory models, please inquire.
Lung fibrosis ex vivo:
For ex vivo analysis of lung fibrosis, we offer Precision Cut Pulmonary Slices (PCPS) models. Like Precision Cut Liver Slices (PCLS) models, PCPS are three-dimensional tissue explants derived from human or animal lungs that can be cultured ex vivo for a certain time. They retain the anatomical architecture of the lung and its specific features, such as tissue homeostasis and, to a certain extent, immunological functions. Each lung provides enough slices to test several experimental conditions in a comparative manner. Due to its ability to closely recapitulate in vivo conditions, we use PCPS as a model for toxicological and pharmaceutical research and as an alternative to animal models in compound screening.

Effect of reference compound (Nintedanib) in PCPS on fibrosis markers (TIMP-1 and WISP-1) after induction of fibrosis for up to 96 hours.
If you are interested in liver fibrosis models, see here for other fibrosis models, please inquire. Our fibrosis platform is complemented by numerous in vitro and ex vivo assays.
Asthma in vivo:
Asthma is a complex and heterogeneous chronic inflammatory disease of the airways, causing a substantial public health problem. Endoytpes of severe asthma can be stratified by the extent of immune cell infiltration, which is either predominantly eosinophilic or neutrophilic or exhibits a mixed neutrophilic/eosinophilic pattern. Given that different asthma endotypes exist, there is a need to reflect these in preclinical animal models used for drug discovery programs.
We offer two different mouse models of house dust mite (HDM)-induced asthma, which reflect either eosinophilic asthma or mixed-granulocytic asthma. Your anti-inflammatory candidate compound(s) can be profiled head-to-head with Standard of Care (SoC) compounds like, e.g., dexamethasone, LABA, and LAMA. We can administer your test compound(s) by different application routes (e.g., oral, subcutaneous, intratracheal, intranasal, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and osmotic pumps).
Read-outs:
- Bronchoalveolar (BAL) fluid analysis with total and differential immune cell counts by FACS analysis.
- Assessment of airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR)
- Lung histopathology
- Cytokine analysis (BAL, lung)
- Biomarker analysis (ELISA, qPCR)
- µCT imaging of the lung
- PK and/or PK/PD analysis
Get in touch with our scientific experts. If you are interested in other respiratory models, please inquire.
Eosinophilic HDM-induced asthma
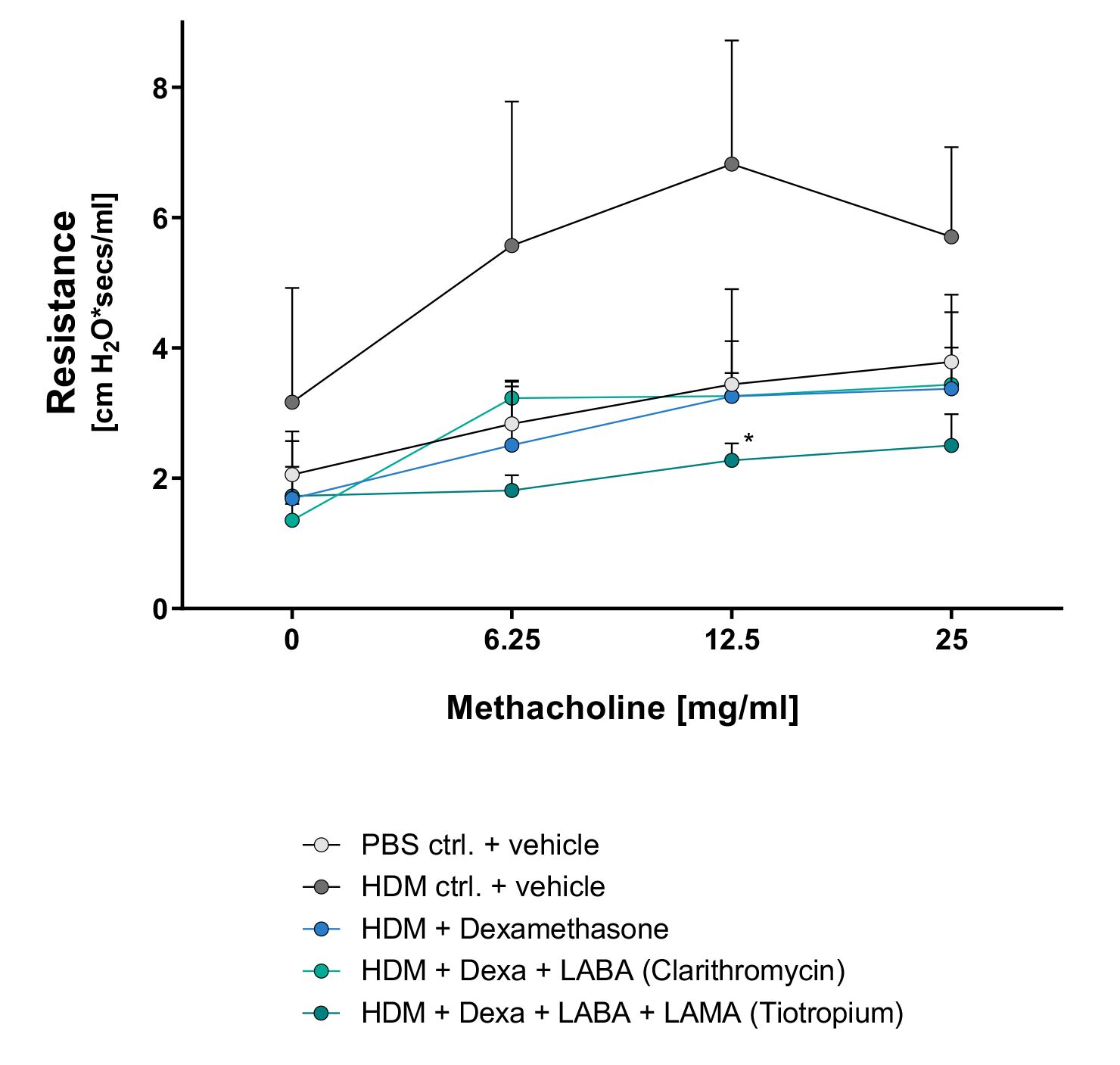
Corticosteroid therapy, alone or in combination with LABA and LAMA, decreased methacholine-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in eosinophilic HDM asthma.
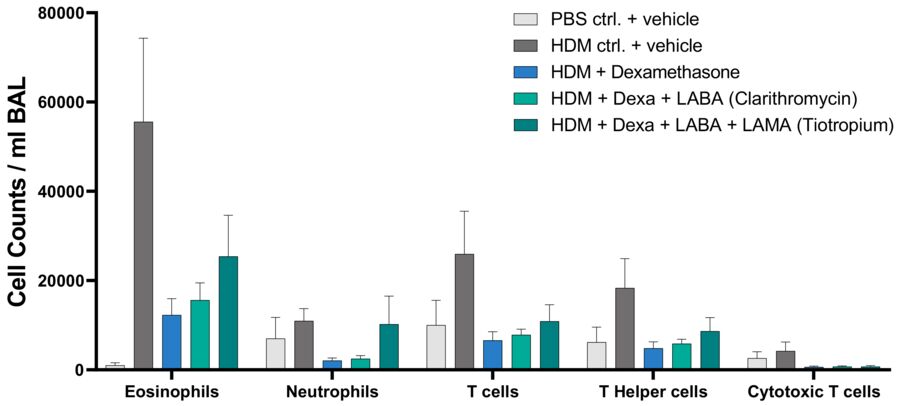
Standard of Cares (SoCs) inhibited differential immune cell count in bronchoalveolar fluid from mice with eosinophilic HDM asthma.
Mixed-granulocytic HDM/CFA-induced asthma

Increased neutrophil counts in the BAL fluid of mixed-granulocytic asthma exhibit reduced steroid responsiveness.




