Proliferation Assays
To monitor viability or proliferation, phenotypes of cell line models can be instrumental for the characterization and selection of drug candidates. Cell lines with endogenous or engineered expression of a selection biomarker (e.g., an oncogenic driver mutation) are highly informative. Examples of mechanistic cellular assays we frequently use in clients’ projects to measure cell proliferation, viability, and apoptosis include:
- 2D proliferation assays (e.g., measuring metabolic activity, ATP levels)
- life cell imaging: Acquisition of phase contrast images of cells using, for example, the IncuCyte® system (automated quantification of cell nuclei or cell confluency)
- 3D proliferation/colony formation assays in methylcellulose, agarose, or in ultra-low attachment plates
- real-time cell energetics (Agilent Seahorse® analyzer)
- drug combination assays (determination of synergistic or additive effects)
- cytotoxic T cell killing/antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- cell apoptosis assays (e.g., Annexin V/PI FACS assay or Caspase 3/7 activation)
- cell cycle analysis/Nicoletti assay (sub-G0/G1 cells)
DNA Damage Assays
NUVISAN has long-standing expertise in DNA damage assays to evaluate the diverse effects of compounds and the underlying molecular mechanisms to repair DNA lesions. We offer assays for the detection, analysis, and quantification of different DNA damage associated phenotypes, as well as DNA damage repair mechanisms. This includes high-throughput layouts, such as our high-content assay platform. We also offer in vitro and in vivo X-ray irradiation capabilities for experimental DNA damage induction. Some example readouts are
- quantification of different DNA damage foci, intensity, and morphology parameters
- several markers established for DNA damage: yH2AX, pATM, RAD51, pRPA, 53BP1, NBS1, MDC1, pKAP
- classical quantification of DNA damage foci (e.g., TUNEL assay)
- optimized image analysis routines to quantify DNA damage vs. general toxic compounds

Cancer cells stained with a DNA damage marker and high-content image analysis.
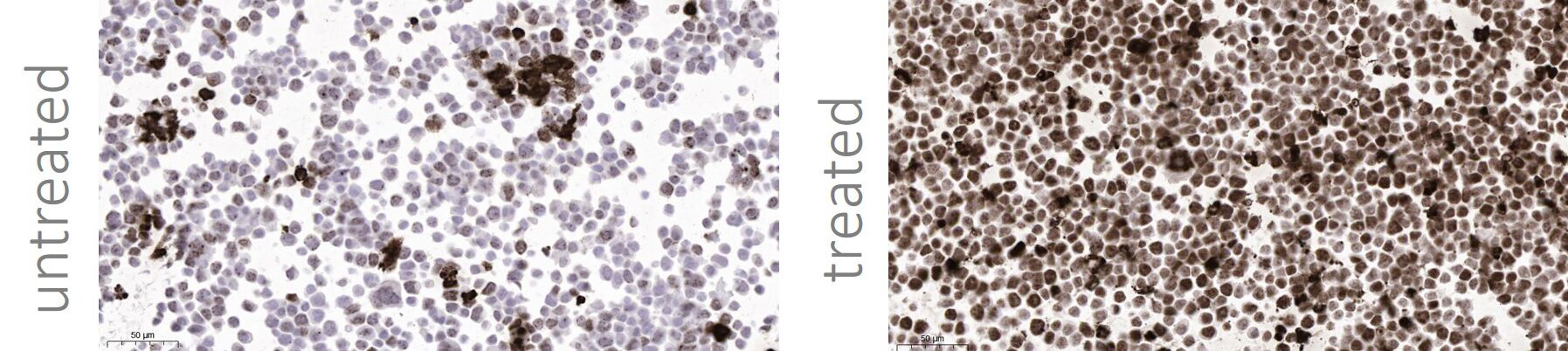
Cancer cells stained with a DNA damage marker phospho-H2AX (pSer139) by IHC.
Scratch (Migration) Assay
Cell migration is essential for many physiological processes, including embryo development, wound repair, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis. The scratch wound assay measures basic cell migration parameters. We use the IncuCyte® system to quantify cells with time-lapse imaging. We offer this assay with different cell types, including cancer model cell lines, primary human fibroblasts (FCs), endothelial cells (ECs), and smooth muscle cells (SMCs).
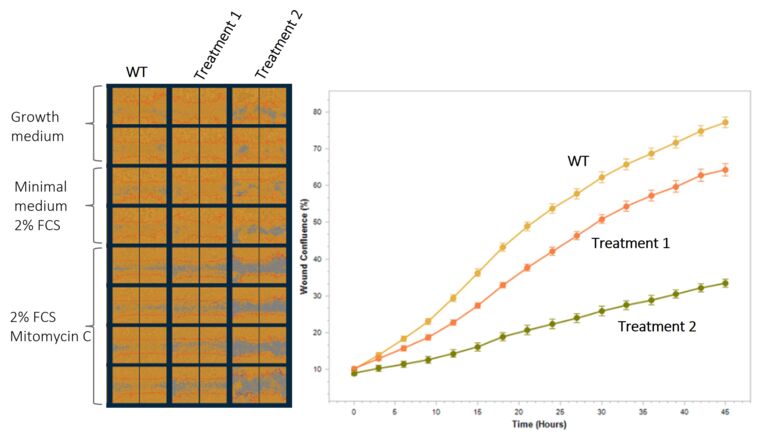
Experiment in MIA PaCa-2 cells, Data generation and analysis using the Incucyte® SX5 Live Cell Analysis Instrument.
Apoptosis
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is frequently disturbed in cancer cells, which means therapies leading to induction of apoptosis are highly attractive. Apoptosis is characterized by defined morphological changes, including cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, loss of nuclear membrane integrity, plasma membrane blebbing, and the formation of apoptotic bodies. These phenotypes can be monitored to confirm the induction of apoptosis by small-molecule drugs or biologics. However, treatment with drugs can often lead to mixed phenotypes that also include necrosis in cancer cells. We offer multiple methods to assess different aspects of the apoptotic pathway and to characterize the mode of action of your compound.
- Caspase 3/7 activation during cell apoptosis
- Increase in cell membrane permeability
- Loss of cell membrane asymmetry by detection of exposed phosphatidylserine on cell surface (detection of fluorescent-tagged annexin V via FACS)
- Cytochrome C release assay
- Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential
- Live cell imaging staining of mitochondrial membrane
- TUNEL assay (DNA fragmentation)
- Measurement of increased double strand breaks via yH2AX (late-stage apoptosis)